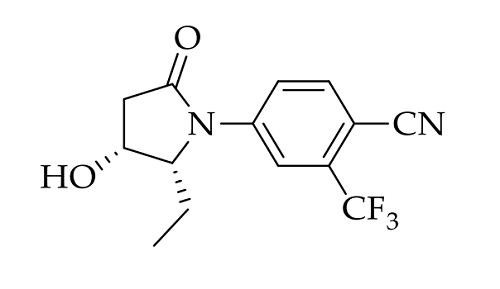
SARM 2f (doping substance )
SARM 2f (Selective Androgen Receptor Modulator) - Doping Analysis
New Publication
Möller T, Wen HC, Naumann N, Krug O, Thevis M.
Identification and Synthesis of Selected In Vitro Generated Metabolites of the Novel Selective Androgen Receptor Modulator (SARM) 2f.
Molecules. 2023 Jul 20;28(14):5541. doi: 10.3390/molecules28145541. PMID: 37513414; PMCID: PMC10385812.
Abstract
Among anabolic agents, selective androgen receptor modulators (SARMs) represent a new class of potential drugs that can exhibit anabolic effects on muscle and bone with reduced side effects due to a tissue-selective mode of action. Besides possible medical applications, SARMs are used as performance-enhancing agents in sports. Therefore, they are prohibited by the World Anti-Doping Agency (WADA) in and out of competition. Since their inclusion into the WADA Prohibited List in 2008, there has been an increase in not only the number of adverse analytical findings, but also the total number of SARMs, making continuous research into SARMs an ongoing topic in the field of doping controls. 4-((2R,3R)-2-Ethyl-3-hydroxy-5-oxopyrrolidin-1-yl)-2-(trifluoromethyl)benzonitrile (SARM 2f) is a novel SARM candidate and is therefore of particular interest for sports drug testing. This study describes the synthesis of SARM 2f using a multi-step approach, followed by full characterization using liquid chromatography–high-resolution mass spectrometry (LC-HRMS) and nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy (NMR). To provide the first insights into its biotransformation in humans, SARM 2f was metabolized using human liver microsomes and the microsomal S9 fraction. A total of seven metabolites, including phase I and phase II metabolites, were found, of which three metabolites were chemically synthesized in order to confirm their structure. Those can be employed in testing procedures for routine doping controls, further improving anti-doping efforts.